Platelet Disorders: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
06-Oct-2023
Platelet Disorders: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
Our blood is a lifeline, coursing through our bodies to supply oxygen, nutrients, and essential components like platelets. These tiny cell fragments play a critical role in our health by helping our blood to clot when we're injured. However, like any aspect of our health, platelets can sometimes go awry, leading to platelet disorders.
In this blog, we'll delve into platelet disorders, exploring their symptoms, diagnosis, and management.
Understanding Platelets
Before we dive into platelet disorders, it's important to understand what platelets are and why they matter. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are one of the key components of blood. Their primary function is to prevent excessive bleeding. When you get injured, platelets rush to the site to form a clot, sealing the wound and preventing further blood loss.
Common Platelet Disorders
Thrombocytopenia: This condition is characterized by a low platelet count. Symptoms may include easy bruising, frequent nosebleeds, and prolonged bleeding from minor injuries.
Thrombocytosis: Thrombocytosis is the opposite of thrombocytopenia. It involves an abnormally high platelet count, which can lead to excessive clotting, potentially causing blood clots.
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP): ITP is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys platelets, leading to a low platelet count. This can result in bruising, nosebleeds, and fatigue.
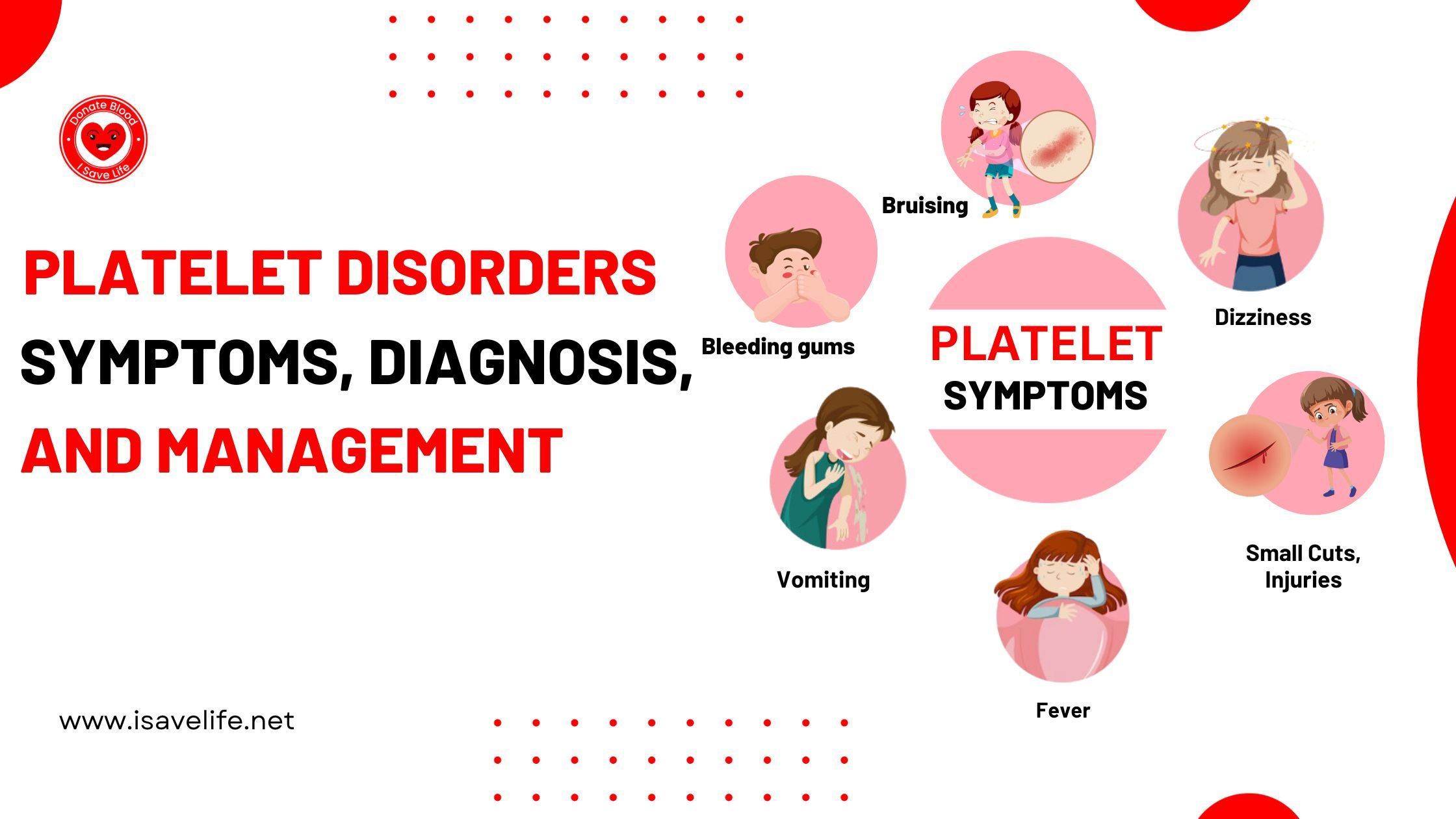
Symptoms of Platelet Disorders
The symptoms of platelet disorders can vary depending on whether the platelet count is too high or too low. Common symptoms include:
Easy bruising
Frequent nosebleeds
Prolonged bleeding from small cuts or injuries
Blood in urine or stool
Fatigue
Bleeding gums
Dizziness
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing platelet disorders involves blood tests to determine platelet count and function. Additional tests may be necessary to identify the underlying cause of the disorder.
Management of platelet disorders depends on the specific diagnosis:
Thrombocytopenia: Treatment may involve addressing the underlying cause, such as an underlying medical condition or medication adjustment. In severe cases, platelet transfusions may be necessary.
Thrombocytosis: Managing thrombocytosis often focuses on addressing the underlying condition and preventing complications like blood clots. Medications to reduce platelet production may be prescribed in some cases.
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP): Treatment aims to raise platelet counts and may include medications, immune-suppressing drugs, or, in severe cases, removal of the spleen.